The Data Protection Process: The 9 Steps to DPA Heaven
A roadmap to effectively safeguard personal data, ensure regulatory compliance, and build lasting trust with stakeholders.
In the interconnected, data-driven landscape of our modern world, a solid data protection strategy is not just an option – it's an absolute necessity. Organisations are entrusted with vast quantities of sensitive data, and with this comes an imperative to handle this data with utmost care and precision. The significance of data protection has only been amplified by rising threats, stricter privacy laws, and increasingly severe consequences for data breaches. The need to be in line with Data Protection requirements is paramount, with both legal and reputational repercussions at stake.
This is why we've developed ""The Data Protection Process: The 9 Steps to DPA Heaven,"" a comprehensive and user-friendly guide that demystifies the process of meeting Data Protection requirements. This guide breaks down the complex roadmap into nine digestible, manageable steps to help organisations not only achieve compliance but also foster a culture of data protection awareness.
Starting with the fundamental step of implementing a data protection policy, this guide moves through carrying out a data protection impact assessment, appointing a Data Protection Officer, and ensuring that staff members are well-versed in their obligations. The journey continues with the specifics of obtaining valid consent for processing data, updating privacy notices, implementing technical safeguards, responding to subject access requests, and finally, reporting any security breaches.
In this article, we will meticulously guide you, the senior stakeholders, through each of these steps. Our goal is to make the DPA compliance process clear, straightforward, and actionable. We aim to empower you with the knowledge to not only navigate but also anticipate and plan for the complexities of data protection. So, whether you're just beginning your journey to data protection or looking to strengthen your existing measures, let's step onto the path to DPA heaven together.
Introduction
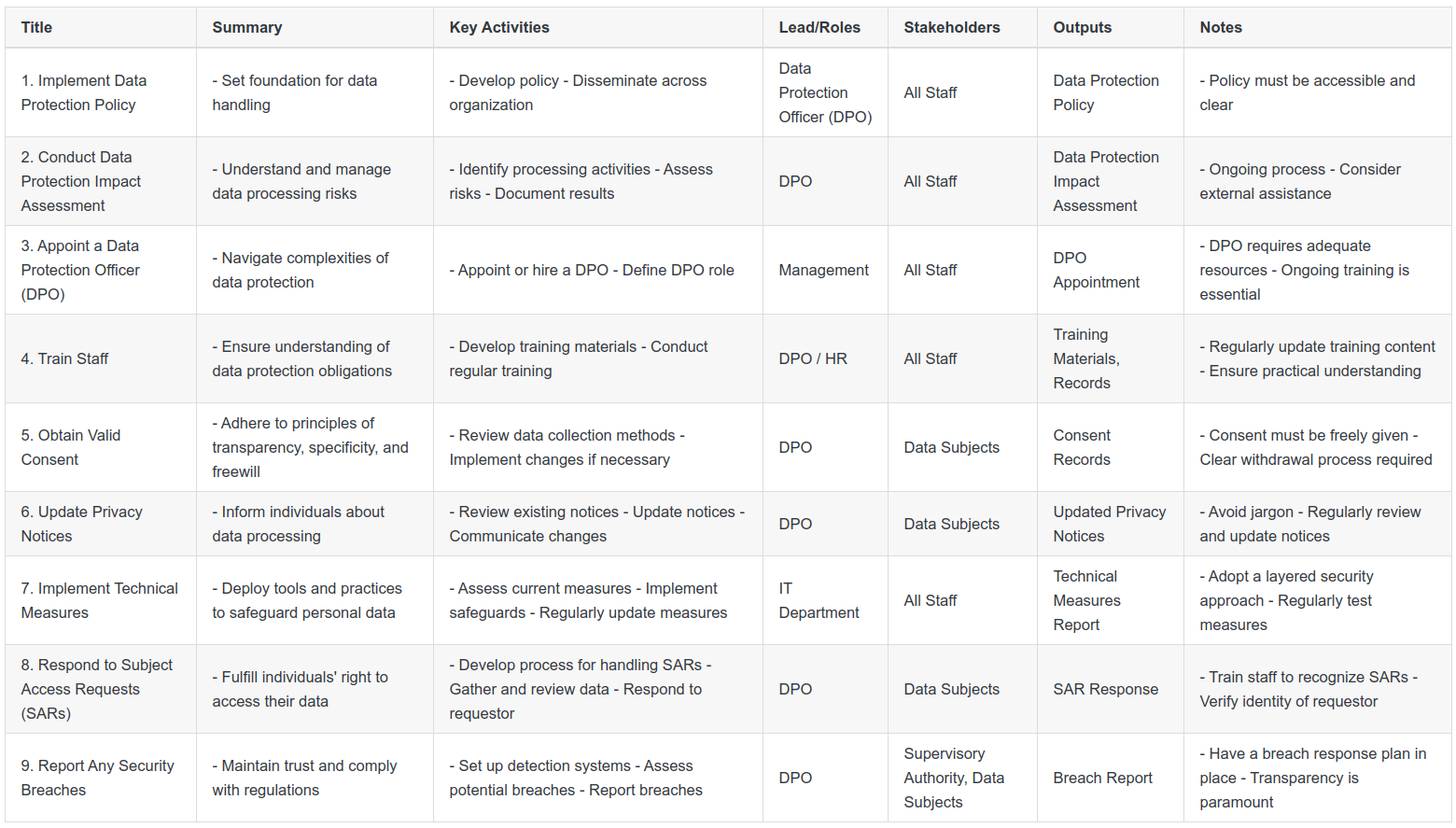
Data protection is an essential part of any organisation's operations, and successfully managing it involves a multi-faceted approach. This approach provides a straightforward, nine-step process, designed to guide you on your journey to full Data Protection compliance.
These steps include:
- Implementing a data protection policy,
- Carrying out a data protection impact assessment,
- Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO),
- Ensuring staff understand their obligations,
- Validating consent for processing,
- Updating privacy notices,
- Implementing technical measures,
- Responding to subject access requests, and
- Reporting any security breaches.
By following these steps, you'll navigate the data protection landscape with ease, ensuring your organisation operates within legislative requirements while safeguarding your precious data assets.
BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Here is a summary of the 9-Step process, that you can follow as we walk through each step.
Step 1: Implement a Data Protection Policy
The foundation of any successful data protection strategy starts with the implementation of a clear, comprehensive, and effective data protection policy. This policy acts as a blueprint for how your organisation handles and safeguards personal data, setting out the 'why', 'what', 'how', and 'when' of data processing activities.
Key Activities
The process begins with understanding the types of data your organisation processes, including personal data and sensitive personal data. This should involve a thorough data mapping exercise that identifies where data comes from, where it is stored, how it is processed, who has access to it, and where it goes when it leaves your organisation.
Next, your policy should outline the data protection principles your organisation adheres to, such as lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimisation, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity, and confidentiality.
Furthermore, your policy should articulate clear procedures for data subject rights, data breach response, data protection impact assessments, and the appointment and responsibilities of your Data Protection Officer (DPO).
Key Roles and Stakeholder Engagement
Key stakeholders in this process include senior management, who are responsible for endorsing the policy, and the Data Protection Officer (if already appointed), who plays a central role in the development and maintenance of the policy. The policy should be communicated to all employees and relevant third parties to ensure everyone understands their responsibilities.
Outputs
The key output of this step is a well-documented Data Protection Policy that is easily accessible to all stakeholders, both internal (such as employees) and external (like customers or users). This policy should be reviewed and updated regularly, at least annually or whenever there is a significant change in your data processing activities or relevant legislation.
Summary
Remember, a data protection policy is not a one-size-fits-all document. It needs to be tailored to your organisation's specific needs, operations, and data processing activities. Moreover, it's essential to remember that a policy on its own isn't enough – it needs to be backed by actual practices.
A useful tip from our experience is to engage all levels of the organisation during the policy development process. This includes everyone from top-level management to those involved in day-to-day data processing. Doing so ensures that the policy reflects practical realities and is embraced by the whole organisation.
Finally, it's always beneficial to seek external expertise when creating your policy, especially if your organisation processes large amounts of sensitive data. Consulting with data protection specialists can ensure your policy is robust, comprehensive, and compliant with the latest legislative requirements.
In summary, implementing a robust data protection policy is the first and crucial step on your journey to Data Protection Heaven. It sets the tone and direction for your data protection efforts and serves as a constant point of reference for all data-related activities within your organisation."
Step 2: Carry Out a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
"The Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is an essential instrument in your data protection toolkit, particularly when it comes to high-risk data processing scenarios. It provides a structured method to analyze, identify and minimize the data protection risks of a project or plan.
Key Activities
Carrying out a DPIA involves several distinct activities. Firstly, it's important to describe the nature, scope, context, and purpose of the data processing. This gives a clear picture of what exactly you're assessing and lays a solid foundation for the rest of the process.
Next, assess the necessity and proportionality of the processing. This means ensuring that you're only processing data that is necessary to achieve your purpose and that you're not holding onto it for longer than needed.
Subsequently, identify and assess the risks to individuals. This could range from potential threats to their privacy, to potential misuse of their data, and even the risk of data breaches.
Finally, identify measures to mitigate those risks. These could be anything from technical measures like encryption, to policy measures such as limiting access to the data.
Key Roles and Stakeholder Engagement
The key stakeholders in carrying out a DPIA are the Data Protection Officer (DPO), who oversees the assessment, and the project team, who will need to understand the outcomes of the DPIA and implement the necessary measures. It may also be necessary to consult with individuals (or their representatives) whose data will be processed, to gain their perspectives on the proposed processing.
Outputs
The primary output from this step is the DPIA report. This document should provide a thorough overview of the data processing operation, highlight potential risks, and propose mitigation measures. This report should be updated regularly, especially if there are changes in the processing operation that may affect the risk to individuals.
Summary
From our experience, one of the best practices when carrying out a DPIA is to start early and update often. It's much easier to address data protection risks during the design stage, rather than retrofitting solutions after a system or process is already in place. This is what's often referred to as ""privacy by design.""
Another tip is to make sure that you're being thorough in your risk assessment. This includes considering both the likelihood and the severity of any potential impact on individuals. Keep in mind that even low-risk scenarios can have a significant impact if they are likely to occur frequently.
Furthermore, don't underestimate the value of external input. Whether it's consulting with data protection experts or seeking the views of the individuals whose data you're processing, these perspectives can help identify risks and solutions that you might not have considered.
Remember, a DPIA isn't just a box-ticking exercise to meet regulatory requirements; it's a valuable tool to help you process data in a way that respects individuals' rights and minimizes risks. By taking the time to carry out a thorough DPIA, you can ensure that your data processing operations are not only compliant, but also more likely to earn the trust of the individuals whose data you're handling."
Step 3: Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
"Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) is a crucial step in complying with Data Protection requirements, particularly for high-risk data processing scenarios. The DPO serves as a central figure in overseeing data protection activities, ensuring compliance, and acting as a point of contact for data subjects and the supervisory authority.
Key Activities
Appointing a DPO begins with identifying the right person for the role. This could be an internal staff member or an external professional. The individual should possess a thorough understanding of data protection laws and practices and be familiar with your organisation's data processing activities.
Next, you'll need to clearly define the DPO's responsibilities. This typically includes advising on data protection laws, monitoring compliance, managing internal data protection activities, training staff, conducting audits, and serving as the primary contact for supervisory authorities and data subjects.
Key Roles and Stakeholder Engagement
The role of the DPO is typically assigned by senior management. The DPO will interact with various stakeholders within the organisation, from those directly involved in data processing to those responsible for managing IT security, legal affairs, and human resources. External stakeholders might include supervisory authorities and data subjects.
Outputs
The key output in this step is the formal appointment of a DPO. This should be documented in writing, specifying their tasks and responsibilities. The contact details of the DPO should also be published where applicable and communicated to the supervisory authority.
Summary
When appointing a DPO, ensure that they are involved properly in all issues relating to the protection of personal data from the start. Their involvement from the early stages of projects can help avoid potential data protection issues down the line.
It's crucial to ensure the DPO is given the necessary resources, access to personal data and processing operations, and the ability to maintain their expert knowledge. Furthermore, the DPO should operate independently and not receive any instructions regarding the exercise of their tasks.
Remember that the DPO's tasks are not just about compliance. They are also about advising, informing, and recommending solutions. It’s important to create an environment where the DPO is seen as a support role rather than a compliance officer.
Lastly, remember that while the DPO plays a crucial role in data protection, responsibility for compliance still ultimately lies with the organisation. All members of the organisation should understand their responsibilities when it comes to data protection.
By appointing a skilled and experienced DPO, your organisation is not only taking a key step towards DPA compliance, but it's also underlining its commitment to data protection. This is a significant move in earning the trust of data subjects and maintaining a strong reputation in the marketplace.
Step 4: Ensure Staff Understand Their Obligations
"An integral part of any data protection strategy involves equipping your staff with the necessary knowledge and skills to handle personal data responsibly. After all, the actions of individuals within an organisation can significantly impact its data protection efforts.
Key Activities
The process begins by establishing a comprehensive data protection training program. This program should cover essential aspects of data protection, including the principles of data protection, the rights of data subjects, recognizing and responding to data breaches, and understanding everyone's role in maintaining data privacy.
Following this, regular training sessions should be scheduled to ensure that all staff are kept up to date with the latest data protection practices and legal requirements. This training should be mandatory for all staff who handle personal data and should be refreshed at regular intervals.
In addition to formal training, creating a culture of data protection is vital. This could include regular reminders about data protection policies, tips for secure data handling practices, and promoting open communication about data protection concerns.
Key Roles and Stakeholder Engagement
Key roles in this process include the Data Protection Officer (DPO) or designated data protection leads, who will be responsible for developing and delivering the training program. All staff members, from senior management to front-line workers, have a role to play in implementing what they've learned in their daily activities.
Outputs
The key outputs from this step are a comprehensive data protection training program and a well-informed workforce. An additional output could be a training completion record or certification that shows who has completed the training and when, which can be vital in demonstrating compliance to regulators.
Summary
One key piece of advice is to ensure that the training is tailored to your organisation and the specific roles of your staff. For example, staff involved in handling customer data may need more detailed training on data subject rights, while those involved in IT might need more focus on data security.
Another best practice is to encourage a proactive approach to data protection. Staff should feel empowered to flag potential data protection issues and should be rewarded for doing so, rather than feeling like they might be punished for highlighting a problem.
Finally, it's crucial to remember that data protection is a moving target. Laws change, new threats emerge, and best practices evolve. So it's important to keep your training program up to date and provide regular refreshers to your staff.
Overall, ensuring your staff understand their data protection obligations is a powerful step in safeguarding personal data. By empowering your staff with the knowledge and skills to handle personal data responsibly, you're turning them from potential weak points into your greatest data protection asset.
Step 5: Ensure You Have Valid Consent for Processing
One of the fundamental principles of data protection is the requirement of consent. If you intend to collect or process personal data, you must have clear and valid consent from the individual. This consent must be informed, freely given, specific, and unambiguous.
Key Activities
The first step in ensuring valid consent is to clearly define what data you are collecting, why you are collecting it, how you plan to use it, and who will have access to it. This information should be clearly communicated to the individual before they give their consent.
Next, design consent forms or mechanisms that are easy to understand and use. The language used should be clear and simple, and it should be just as easy for an individual to withdraw their consent as it is to give it.
Furthermore, ensure that you have systems in place to keep clear records of consent. This includes when and how the consent was obtained and any subsequent changes or withdrawals of consent.
Lastly, regularly review and refresh consent as necessary. This is especially important if there's a change in the way you process data, or at regular intervals to ensure the continued engagement of the individual.
Key Roles and Stakeholder Engagement
Key roles in this process include the DPO or data protection leads who design the consent processes and maintain records, and frontline staff who often handle the direct collection of consent from individuals. Stakeholders include the individuals from whom consent is being sought.
Outputs
The primary output from this step is a record of consent for all processed personal data. This includes documentation of who gave consent, what they were told, how they gave consent, and when. The secondary output is an easy-to-use and understandable consent mechanism (like a consent form or checkbox).
Summary
One best practice is to make consent an active process. Don't rely on pre-ticked boxes or inactivity as a sign of consent – the individual should make a clear action to give their consent.
Additionally, always be transparent about your data practices. If an individual fully understands what they're consenting to, they're more likely to trust your organisation with their data.
A useful tip is to ensure that withdrawing consent is as easy as giving it. If an individual decides they no longer want their data processed, respect their decision and have a clear process for handling this.
Finally, remember that consent is only one of the legal bases for processing personal data, and in some cases, it might not be the most appropriate one. Always consider the nature of your data processing activities and the rights and freedoms of the individual when determining your legal basis.
In conclusion, ensuring valid consent is not just about compliance with data protection laws; it's also a matter of respect for individuals' rights and building trust with them. By making consent a priority, you can demonstrate your commitment to responsible data handling and enhance your reputation as a trusted organisation.
Step 6: Update Privacy Notices
Your organisation's privacy notices serve as a cornerstone of transparency and trust with individuals whose personal data you process. They provide critical information about how you handle personal data and what rights individuals have. Therefore, ensuring these notices meet all Data Protection Act (DPA) and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requirements is essential.
Key Activities
Begin by reviewing your existing privacy notices. Check for clarity, completeness, and compliance with data protection legislation. This includes ensuring the notice provides adequate information about what personal data you collect, how and why you use it, who you share it with, how long you keep it, and what rights individuals have in relation to their data.
Next, make any necessary updates or changes. This could involve rewriting parts for clarity, adding missing information, or updating outdated sections. The language used should be straightforward and accessible to a non-expert audience.
After making these updates, communicate the changes to the individuals whose data you process. You might do this by email, through your website, or via other means appropriate to your context. Make sure the updated privacy notices are easy to find and read.
Key Roles and Stakeholder Engagement
The Data Protection Officer (DPO) or designated data protection lead typically spearheads the privacy notice update. It's also beneficial to involve legal counsel to ensure that the privacy notice meets regulatory requirements. The stakeholders in this case are all individuals whose personal data you process, as they need to be informed about the contents of the privacy notice.
Outputs
The key output from this step is an updated privacy notice that fully meets DPA and GDPR requirements. You should also keep a record of the versions of your privacy notice and when updates were made.
Summary
Ensure your privacy notice is easy to understand. Avoid jargon and legalistic language; the goal is to inform, not confuse.
Make sure you clearly explain the legal basis for processing personal data, whether it's consent, a contractual requirement, or a legitimate interest. And don't forget to detail individuals' rights regarding their data, such as the right to access, rectify, or erase their data, and how they can exercise these rights.
Another tip is to use layered notices or just-in-time notices to provide information to individuals when they need it. For example, you might provide a brief notice when you first collect data, with a link to a more detailed notice.
And remember, updating privacy notices isn't a one-time task. It's something you should revisit regularly, especially if there are changes in how you process data.
Maintaining clear, accurate, and up-to-date privacy notices is not just a regulatory requirement. It's also an opportunity to enhance trust and transparency with individuals and show them that you respect their privacy and data rights.
Step 7: Implement Technical Measures
Technical measures are the backbone of any data protection strategy. They include the tools, systems, and practices that protect personal data from unauthorized access, unlawful processing, accidental loss, destruction, or damage. This step involves setting up and maintaining these measures to ensure robust data security.
Key Activities
Begin by assessing your current technical measures and identifying any gaps or vulnerabilities. This can be done through activities like risk assessments or penetration testing.
Next, implement necessary safeguards. These may include access controls to limit who can access personal data, encryption to protect data during transmission and at rest, and secure data disposal methods. Also, consider implementing intrusion detection systems and firewalls to protect against external threats.
Regular data backups are crucial to prevent data loss in case of accidents or system failures. Ensure you have a robust backup system in place that copies and stores data securely.
Lastly, maintain and regularly update these technical measures. This includes regular software updates, security patches, and system reviews to ensure continued data protection.
Key Roles and Stakeholder Engagement
This step involves your IT department or IT service provider, who will be responsible for implementing and maintaining these technical measures. The DPO or data protection leads should oversee this process to ensure it meets data protection requirements.
Outputs
The outputs from this step include a detailed report of the technical measures implemented, an updated risk assessment document reflecting the reduced risk due to these measures, and a backup and recovery plan. Records of regular maintenance activities and software updates should also be kept as proof of ongoing data protection efforts.
Summary
One best practice is to adopt a layered security approach. Don't rely on a single measure to protect your data; use a combination of measures to provide multiple barriers against threats.
Another tip is to implement 'privacy by design and by default'. This means considering privacy at the initial design stages of any new system, service, or process that involves personal data.
Remember to regularly test your security measures, including your backup and recovery systems. This can help you identify any weaknesses before they can be exploited and ensure your systems are working as expected.
Lastly, make sure your technical measures align with your data protection policies. They should work together to provide a comprehensive and effective data protection strategy.
In conclusion, implementing robust technical measures is essential in safeguarding personal data and maintaining trust in your organisation. With these controls in place, you can confidently assure individuals that their data is safe in your hands.
Step 8: Respond to Subject Access Requests
A fundamental aspect of data protection is allowing individuals to understand what personal data you hold about them. This is often done through subject access requests (SARs), which require efficient and accurate handling. Here's how you can effectively manage this process:
Key Activities
The initial step is to develop a streamlined process for recognizing and handling SARs. An SAR can be made through any channel, so it's essential that all staff members understand what these requests look like and how they should be processed.
Once a request is identified, it should be forwarded to the relevant team or person for handling, often the Data Protection Officer (DPO) or designated data protection lead.
This person should then locate the relevant data, ensuring all requested information is gathered. This process may involve searching databases, email records, and physical files.
After the data is gathered, review it to ensure it can be released. Sometimes, data might include information about other individuals or sensitive business information that cannot be shared.
Finally, respond to the requestor with the data in a concise, transparent, and easily understandable format, usually within one month of the request being made.
Key Roles and Stakeholder Engagement
Key roles include frontline staff who may receive SARs, the DPO or data protection lead who handles the request, and IT staff who may need to assist with data retrieval. The key stakeholder here is the individual making the SAR.
Outputs
The main output from this step is the response to the SAR. This should include all the requested information that can be shared, as well as any necessary explanations or context. Also, a record of the SAR and its response should be kept for future reference or in case of disputes.
Summary
Training your staff to recognize an SAR is crucial. SARs do not have to be made in a specific format or even explicitly state that they are SARs.
Another best practice is to verify the identity of the requestor before providing the information to prevent unauthorized disclosure of personal data.
It's also a good idea to establish a centralized system for managing SARs. This can help streamline the process, prevent delays, and ensure a consistent response.
Remember that a reasonable fee can only be charged for repetitive or unfounded requests. For most SARs, you should provide the information free of charge.
In conclusion, effectively managing SARs is not only a legal requirement but also a chance to demonstrate your organisation's commitment to transparency and individual rights. With a well-planned and executed process, you can turn SARs into a positive experience for both your organisation and the individuals involved.
Step 9: Report Any Security Breaches
The unfortunate reality of the digital age is that data breaches occur. What's important is how your organisation responds. GDPR requires organisations to report certain types of personal data breaches to the relevant supervisory authority. Here's how you can ensure compliance and maintain trust in your data protection strategy:
Key Activities
The first key activity is to set up systems to detect and monitor for security breaches. This could involve using software tools, conducting regular security audits, or training staff to recognize potential breaches.
When a potential breach is detected, it's important to swiftly assess the situation. Determine the nature and extent of the breach, and the potential impact on personal data and individuals' rights and freedoms.
If the breach poses a risk to these rights and freedoms, you must report it to your relevant supervisory authority. This report must usually be made within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach.
Moreover, if the breach poses a high risk to individuals, you may also need to inform them directly. This notification should be clear and concise, and provide information on the nature of the breach, the likely consequences, and what measures have been or will be taken.
Key Roles and Stakeholder Engagement
The Data Protection Officer (DPO) or data protection lead typically oversees this process, but IT staff, HR, and management also play critical roles in detecting, investigating, and managing breaches. The relevant supervisory authority and affected individuals are the key stakeholders in this process.
Outputs
The key outputs from this step are the breach report submitted to the supervisory authority and the notification to affected individuals, if required. Also, keep a record of all breaches, regardless of whether they were reported, to inform future risk assessments and security measures.
Summary
One key piece of advice is to have a breach response plan in place. This helps ensure a quick, coordinated, and effective response when a breach occurs.
Regular training can also help staff understand the types of incidents that need to be reported and how to report them.
Transparency is paramount when handling data breaches. It's not only a regulatory requirement but also crucial for maintaining trust with individuals and mitigating reputational damage.
In conclusion, the ability to effectively respond to and report data breaches is a key part of any data protection strategy. Through prompt and transparent actions, you can uphold your legal obligations and demonstrate your commitment to data protection.
Ascending to Data Protection Heaven
Embarking on the journey of data protection can seem daunting, but when broken down into manageable steps, it becomes much more achievable. The nine-step process we have just outlined is your stairway to ""Data Protection Heaven.""
We started with implementing a robust data protection policy, setting the foundation for how your organisation handles personal data. The second step was to conduct a Data Protection Impact Assessment, ensuring you understand and manage the risks associated with data processing.
The third step was to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO), a crucial figure who navigates the complexities of data protection on behalf of your organisation. Following this, we stressed the importance of ensuring all staff members understand their obligations regarding data protection, achieved through comprehensive training and clear communication.
Step five outlined the necessity of obtaining valid consent for processing personal data, adhering to the principles of transparency, specificity, and freewill. In step six, we emphasized the importance of keeping your privacy notices up to date, ensuring individuals are well-informed about their data processing.
Our seventh step focused on implementing technical measures, deploying tools, and practices to safeguard personal data from unauthorized access and accidental loss. In step eight, we learned about responding to subject access requests, fulfilling individuals' right to access their data.
Finally, the ninth step involved the reporting of any security breaches, reinforcing the importance of transparency and immediate action in maintaining trust and complying with regulations.
These steps provide a systematic approach to meeting Data Protection requirements, offering a comprehensive yet straightforward framework for those tasked with managing personal data. They are not just for Data Protection Officers or IT professionals but for anyone in an organisation who interacts with personal data.
Through following these steps, your organisation can comply with legal requirements, reduce the risk of breaches, maintain trust with customers and stakeholders, and ultimately, create a secure data environment. Each step brings you closer to your destination: a state of data protection nirvana, or as we have playfully titled it, ""Data Protection Heaven.""
The road may have its complexities, but by adhering to this process, you make the journey a manageable and rewarding experience. Welcome to Data Protection Heaven, where compliance, trust, and security live in harmony. Safe travels on your data protection journey!
Further Reading
There remains plenty of suporting materials and guides to help your journey. Here is a list of a few we recommend, if you are looking for wider details to support implementation. Be aware of the publication dates and any potential changes in legislation since publication. Please consider the reliability and reputation of the sources, discretion as always should be used with any article.
- "The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Overview and Compliance Guide" - European Commission. Link
- "Data Protection: A Practical Guide to UK and EU Law" - Peter Carey. ISBN: 978-0198702036 (Published: 2018). Link
- "Understanding the GDPR: A Comprehensive Guide" - IT Governance. Link
- "Guide to the General Data Protection Regulation" - Information Commissioner's Office (ICO). Link
- "Privacy by Design: The Definitive Workshop" - Ann Cavoukian. (Published: 2011). Link
- "Data Protection Impact Assessments: A Practical Guide" - Paul Voigt, Axel von dem Bussche. ISBN: 978-3319995404 (Published: 2018). Link
- "A Practical Guide to Data Protection Audits" - Stewart Room. ISBN: 978-1784514085 (Published: 2016). Link
- "Subject Access Requests under GDPR" - Bird & Bird. Link
- "Preparing for a Personal Data Breach" - Information Commissioner's Office (ICO). Link
- "Data Protection Officer: Profiling and Training the DPO under the General Data Protection Regulation" - Paul Lambert. ISBN: 978-1526509322 (Published: 2018). Link
- "Data Protection: Law and Practice" - Rosemary Jay. ISBN: 978-0414063535 (Published: 2017). Link
- "Implementing Information Security based on ISO 27001/ISO 27002" - Jan De Clercq. ISBN: 978-9087536589 (Published: 2013). Link
- "ISO 27001 Annex A Controls in Plain English: A Step-by-Step Handbook for Information Security Practitioners in Small Businesses" - Dejan Kosutic. ISBN: 978-9538155739 (Published: 2017). Link
- "Data Protection: Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance" - David G. Hill. ISBN: 978-1439815454 (Published: 2009). Link
Links
- You can listen to this article as an audio podcast here.
This article is serialised into 9 seprate podcats and articles.